Small Scale Turbulence code
Development of a Python analytical code allowing to modelise the magnetic turbulence generated by Cosmic Ray instabilities and damped by interaction with a partially ionized plasma. The following equation is solved:
\[\Gamma_\mathrm{g} + \Gamma_\mathrm{in} = 0\]where \(\Gamma_\mathrm{g}\) corresponds to the magnetic turbulence growth rate and depends mainly on the Cosmic Rays distribution, energy and pressure gradient, and \(\Gamma_\mathrm{in}\) corresponds to the magnetic turbulence damping rate which mainly depends on the physical properties of the plasma we consider the waves are propagating in: density, temperature, ionization rate, turbulence rate. Each of both terms is subject to a deep bibliographical theoretical and experimental study. The models of wave growth and damping are then implemented in the code and allow to solve the above equation.
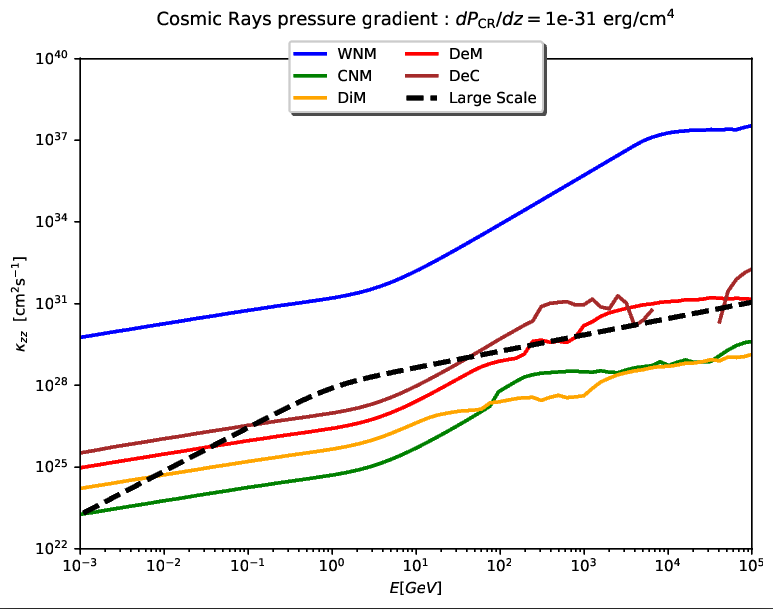
Because Cosmic Rays are charged particles (here we consider protons), they are sensible to magnetic turbulence and their propagation properties are also affected by magnetic turbulence. Depending on the interstellar medium phase I have chosen, I have been able to calculate the mean free path of Cosmic Rays as a function of their kinetic energy for my small scale turbulence model (continuous colored lines) and compare it with the standard model which doesn’t take in account medium properties (black dashed line).
More details here.
